Kubernetes: A Beginner's Guide to Container Orchestration
Published on: November 19, 2025
Updated on: November 19, 2025
min read
What is Kubernetes?
kubernetes is an open source container orchestration plateform which helps to deploy, manage, scale automaticaly our application.
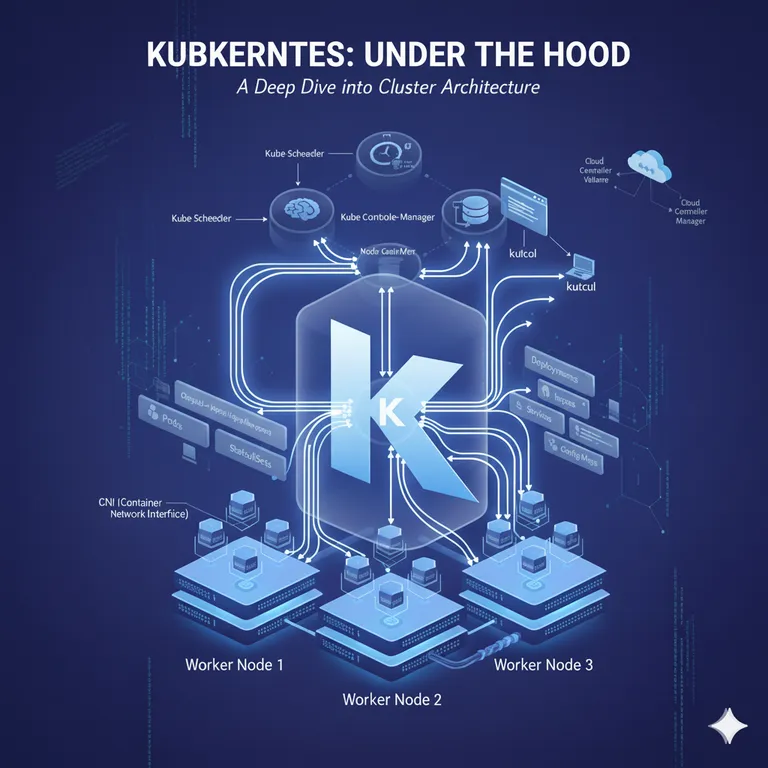
Archetecture of Kubernetes:
kubernetes works in cluster.
Cluster is a set of nodes, in which we have one Controleplane and one or more worker nodes.
Controle Plane
controleplane is the master plane of the kubernetes. Controle plane has some of the components :
-
kube-apiserver:
apiserver is the brain of control plane. when we execute command it will first go to the apiserver. api server works in three stages -
-
Authentication - when request comes to apiserver it will first authenticate user based on certificate or bairer token so that user is the right person or not for that.
-
Authorization - once authentication completed then it authorize the user, using RBAC.
- Admission - After completed 2nd part it will check admission (like- policies) -
It has two webhooks-
-
mutating webhook - we use mutating policies for perticular image . once we have all policies right we move forward.
-
validating webhook - when it will check all the required policies it validates the user to work and save the request to etcd.
-
ETCD:
Etcd is the distributed key value database. It stores all the state about the cluster. ex- how many pods are running, what is the health state of pod etc.
-
Scheduler:
Scheduler is responsible to select the best fit node to create pod based on tent and tolration, affinity and nodeselectore updates the pod spec with node. If pod failed scheduler will recreate another pod. it always check the pod.
-
Controller Manager:
Runs controller process like-
- Node controller
- Replication controller
- Endpoints controller
- and service account
-
Cloud Controller Manager:
It is responsible for cloud related services, manage pv, pvc, loadbalancer etc.
Worker Node
Worker node have three components
-
Kubelet -
Kubelet runs on each node in the cluster, it takes order and responce to the apiserver, makes sure containers are running in the pod.
-
Runtime -
It is a software that responsible for running containers. there are multiple runtimes including containerd, cri-o and Docker, flannel, cilium,calico.
-
Kube-proxy -
Kube-proxy maintains network rule on nodes. These network rules allows network communication to your pod from network session inside or outside of your cluster.
iptables or ipv4
Everytime a pod is created the ip table is handled by kube-proxy.
Core Concept: Pod
Pod is the smallest deployable unit in kubernetes, it contains one or more containers that are deployed together on the same node and share and share the same network storage.
Kubernetes Objects
Deployments
Deployment is an object of kubernetes that helps to deploy, manage, and rollback.
It helps to describe the desired state for pods.
Replicaset:
Replicaset is a object in kubernetes that ensures a specified number of identical pod are always running. If pod deleted or manually or by accident it will recreate them, also distribute the trafic over the multiple replicas.
Statefullset:
A statefulset is a kubernetes controller used to manage stateful applications. those applications need to stable identity,stable storage, ordered the deployment.
Networking
Services
An abstract way to expose application running on a set of Pods as a network service.
Type: ClusterIP, NodePort, LoadBalancer, ExternalName.
Ingress
Ingress is an API object that manages external access to the services in a cluster, typically HTTP.
Storage - Persistent data
PersistentVolume:
It is the actual cluster storage on the cloud
PersistentVolumeClaim:
A request for storage by the pod,PVC bounds to a PV.
Security basics
RBAC:
Role base access control, it defines the access based on the role, what role user have.
NAMESPACE:
namespace is isolated group to work application without conflict in cluster.
Initcontainers:
Init containers are used to download files or other utilities. These containers runs before main container. these containers runs and die. These containers can be multiple.
Sidecar container:
Sidecar containers are use to debug, checking pods health. These containers run together main container.
Best Practices:
Kind
Kind is a tool to run kubernetes locally.
Kubectl
Kubectl is a command line tool to interact with kubernetes cluster.
Basic Kubernetes Commands
# Get cluster information
kubectl cluster-info
# Get nodes in the cluster
kubectl get nodes
# Create a deployment
kubectl create deployment nginx --image=nginx --dry-run=client -oyaml
# Expose a deployment as a service
kubectl expose deployment nginx --port=80 --type=LoadBalancer
# Create a pod
kubectl run nginx --image=nginx